Single Sign-On (SSO) is an authentication method that allows users to access multiple applications with a single set of credentials. The main advantage of SSO is that it makes it easier for your employees to access the resources they need, as they only need to remember one set of login information, which can lead to increased productivity as employees spend less time logging in and more time doing their work. SSO can improve security by reducing the number of passwords employees need to remember and manage. When your employees have fewer passwords to remember, there is a lower risk of choosing weak or easily guessable passwords or reusing the same password across multiple systems.
Another advantage of SSO is that it can reduce the number of password-related help desk calls and improve the overall user experience. When employees only have one set of credentials to remember, they are less likely to forget their passwords, which can reduce the number of password reset requests.
Additionally, SSO can offer Internet Service Providers a way to control employee access to various systems. By using SSO, IT departments can manage employees’ access rights in a centralized manner, making it easier to revoke access when necessary. Implementing Single Sign On can be especially useful for ISPs with many employees or employees working remotely.
There are different types of SSO available, Active Directory or SAML based SSO. Depending on your organization’s setup or requirement, you may want to check which type is better for your business.
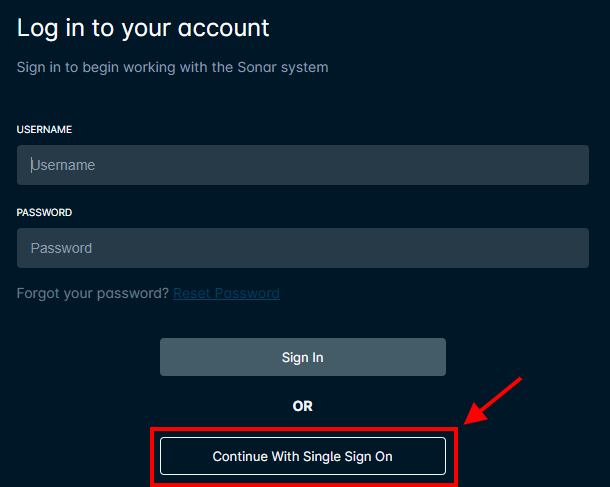
Sonar now offers Auth0, which allows you to add authentication services to your applications. With SSO integrated into your Sonar instance, employees would select continue with Single Sign On instead of inputting their Sonar login credentials. Learn how to configure Auth0 with your Sonar instance.
Final Thoughts
Single Sign On helps improve employee productivity and experience by reducing the number of times they need to enter their login information while also reducing administrative overhead, improving security, and providing a central point of control for managing user access.




